|
|
|
|
Adaptive multiple subtraction using regularized nonstationary regression |
|
|---|
|
lpf
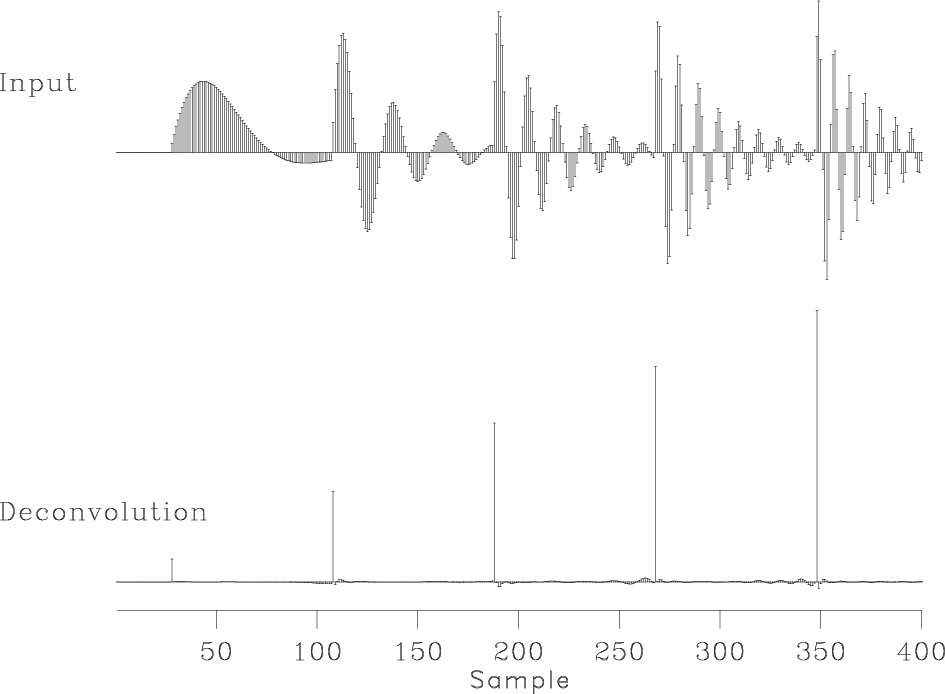
Figure 8. Benchmark test of nonstationary deconvolution from Claerbout (2008). Top: input signal, bottom: deconvolved signal using nonstationary regularized regression. |
|
|
Figure 8 shows an application of regularized nonstationary
regression to a benchmark deconvolution test from Claerbout (2008). The
input signal is a synthetic trace that contains events with variable
frequencies. A prediction-error filter is estimated by setting ![]() ,
,
![]() and
and ![]() . I use triangle smoothing with a
5-sample radius as the shaping operator
. I use triangle smoothing with a
5-sample radius as the shaping operator ![]() . The deconvolved
signal (bottom plot in Figure 8) shows the nonstationary
reverberations correctly deconvolved.
. The deconvolved
signal (bottom plot in Figure 8) shows the nonstationary
reverberations correctly deconvolved.
|
|---|
|
freq
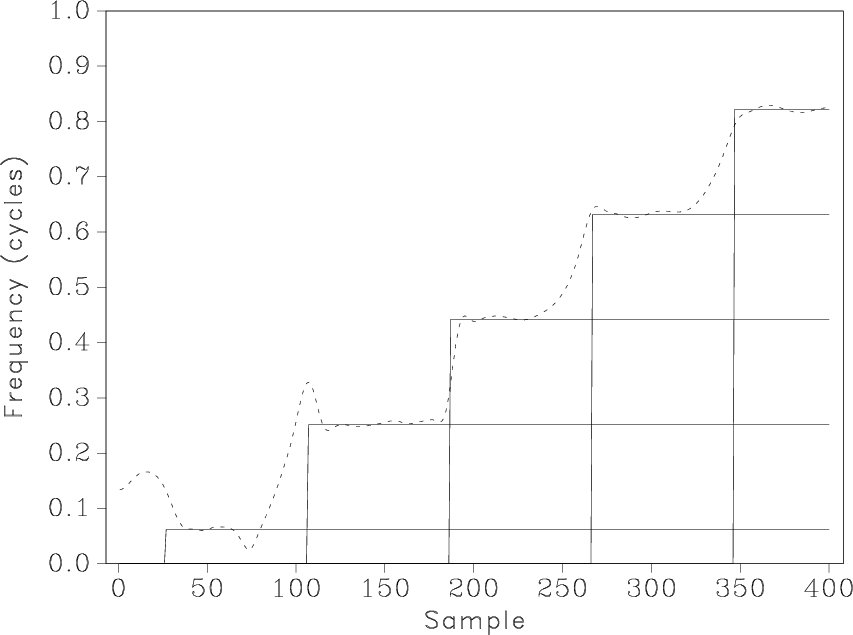
Figure 9. Frequency of different components in the input synthetic signal from Figure 8 (solid line) and the local frequency estimate from non-stationary deconvolution (dashed line). |
|
|
A three-point prediction-error filter ![]() can predict an
attenuating sinusoidal signal
can predict an
attenuating sinusoidal signal
| (11) |
According to equations 9-10, one can get an
estimate of the local frequency ![]() from the non-stationary
coefficients
from the non-stationary
coefficients
![]() and
and
![]() as follows:
as follows:
|
|
|
|
Adaptive multiple subtraction using regularized nonstationary regression |