|
|
|
|
Solving 3D Anisotropic Elastic Wave Equations on Parallel GPU Devices |
When solving the 3D elastic WE on large-scale model domains (i.e.,
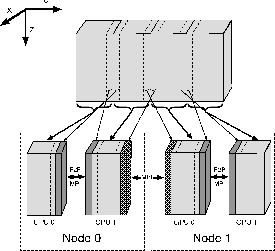
![]() ), the limited global memory of an individual GPU precludes storage of the entire grid on a single device. To parallelize our 3D FDTD algorithm across multiple GPUs, we adopt a domain-decomposition scheme, illustrated in Figure 3, that divides the computational grid in the slowest varying
), the limited global memory of an individual GPU precludes storage of the entire grid on a single device. To parallelize our 3D FDTD algorithm across multiple GPUs, we adopt a domain-decomposition scheme, illustrated in Figure 3, that divides the computational grid in the slowest varying ![]() -axis direction and assigns the sub-domains to separate GPU devices. Each GPU individually executes Steps 1-9 on its assigned sub-domain, whilst CPU-based control threads coordinate the operations of the multiple devices, enable inter-device communication, and combine results to produce the output data.
-axis direction and assigns the sub-domains to separate GPU devices. Each GPU individually executes Steps 1-9 on its assigned sub-domain, whilst CPU-based control threads coordinate the operations of the multiple devices, enable inter-device communication, and combine results to produce the output data.
|
|---|
|
domainDecomp
Figure 3. Schematic of the domain decomposition of the computational grid along the |
|
|
Because the FD stencil in Figure 1 requires data from points extending four units in the forward and backward y-axis directions, the GPU threads that apply the stencil to points along the sub-domain edges may require data from a logically adjacent device. Therefore, boundary data from adjacent sub-domains must be exchanged between GPUs at every time step. This communication can be expensive due to the limited bandwidth of the PCIe bus within a node and/or the network connections between nodes in a distributed system.
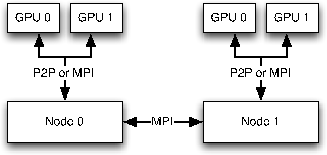
In a consolidated multi-GPU computing environment where all devices share a common PCIe bus, the P2P protocol in NVIDIA's CUDA v4.0 (assuming a GPU with compute capability of ![]() 2.0) can be used to directly exchange data between devices. For a distributed GPU environment, direct P2P communication is not possible as the devices neither share a common PCIe bus nor have direct access to the network. Therefore, as shown in Figure 4, the CPU-based control threads must use the MPI communication interface (or equivalent) to enable communication over the network.
2.0) can be used to directly exchange data between devices. For a distributed GPU environment, direct P2P communication is not possible as the devices neither share a common PCIe bus nor have direct access to the network. Therefore, as shown in Figure 4, the CPU-based control threads must use the MPI communication interface (or equivalent) to enable communication over the network.
|
|---|
|
MPIp2p
Figure 4. Schematic showing distributed computing environment where MPI is used to communicate between nodes, and either MPI or (hybrid) P2P communication is used within a node. |
|
|
By eliminating system memory allocation and copy overhead, direct P2P memory transfer reduces total compute time by ![]() when compared to using MPI-based send/receive commands within a consolidated compute node. In a hybrid environment of distributed multi-GPU compute nodes, a hybrid communication scheme can be adopted where each node uses a single CPU control thread for managing local GPUs (utilizing P2P transfers between devices) while communicating when necessary with remote GPUs via the MPI sub-system. However, for the sake of simplifying our released codes and reproducible examples, we refrain from discussing this situation in more detail herein.
when compared to using MPI-based send/receive commands within a consolidated compute node. In a hybrid environment of distributed multi-GPU compute nodes, a hybrid communication scheme can be adopted where each node uses a single CPU control thread for managing local GPUs (utilizing P2P transfers between devices) while communicating when necessary with remote GPUs via the MPI sub-system. However, for the sake of simplifying our released codes and reproducible examples, we refrain from discussing this situation in more detail herein.
|
|
|
|
Solving 3D Anisotropic Elastic Wave Equations on Parallel GPU Devices |